Spring Force
Spring Force: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Spring Forces, Parallel Arrangement of Springs, Series Arrangement of Springs, Cutting of Springs in a Ratio, Arrangement of Springs, Effective Force Constant, and Effect of Cutting of Springs and Strings in System.
Important Questions on Spring Force
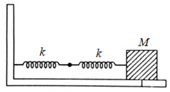
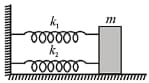
If and respectively are effective spring constant in series and parallel combination of springs as shown in the figure, find
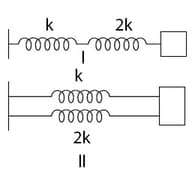
A light spring of force constant is cut into two equal halves and the two are connected in parallel; the equivalent force constant of the system is
A light spring of constant is cut into two equal parts. The spring constant of each part is
In a spring-mass system, the length of the spring is , and it has a mass attached to it and oscillates with an angular frequency . The spring is then cut into two parts, one (a) with relaxed length and the other (b) with relaxed length . The force constants of the two springs and are
When, two ends of an ideal spring are pulled apart increasing its length it produces force equal to at its ends. At a point of its length from one end, the force is
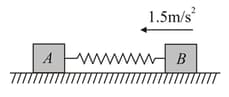
Two blocks with mass and respectively are connected by a stretched spring of negligible mass as in figure. When the two blocks are released simultaneously the initial acceleration of is westward. The acceleration of is:
Two springs of force constants (Spring A) and (Spring B) are joined together in series. The combination is compressed by . The ratio of energy stored in and is Then is equal to:
In a molecule, the can be treated on infinite mass and oscillating alone. If the oscillation of molecule shows frequency of the value of force constant is (take Avogadro number
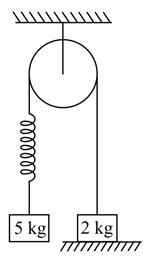
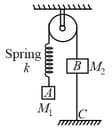
The system shown in the figure is released from rest. Pulley and spring are massless and friction is absent everywhere. The speed of block when block leaves the contact with ground is
A mass is suspended by two springs of force constants and respectively as shown in the diagram. The total elongation (stretch) of the two springs is
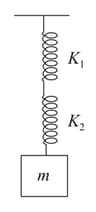
What will be time period of the displaced body of mass ?
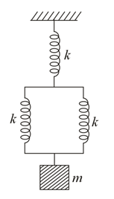
A trolley of mass is connected to two identical springs of spring constant as shown in the figure. The trolley is displaced from its equilibrium position by and released. Find the maximum speed of the trolley in the ensuing motion.
A solid cylinder of mass is rolling on a horizontal smooth surface with velocity . It strikes with a fixed horizontal spring of force constant . The maximum compression produced in the spring is
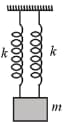
In an elevator, a system is arranged as shown in the figure. Initially, the elevator is at rest and the system is in equilibrium with the middle spring unstretched. When the elevator accelerates upwards, it was found that for the new equilibrium position (with respect to the lift), the further extension in the top spring is times that of the further compression in the bottom spring irrespective of the value of acceleration.
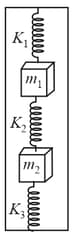
If and and the acceleration of the elevator is , find the tension in the middle spring in final equilibrium with respect to the lift.
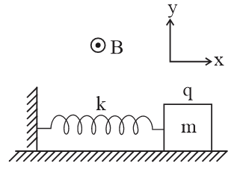
A spring of force constant is fixed at one end and has a small block of mass and charge attached at the other end. The block rests over a smooth horizontal surface. A uniform and constant magnetic field exists in space normal to the plane of the figure. Also an electric field is switched on at sec where is a positive constant. If the block moves on horizontal surface without ever lifting off the surface then the normal reaction acting on the block is-
You are riding in an automobile of mass. Assuming that you are examining the oscillation characteristics of its supension system. The suspension sags when the entire automobile is placed on it. Also, the amplitude of oscillation decreases by during one complete oscillation. Estimate the value of the spring constant.
Match the Column I with Column II:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
|
||
 |
|||
 |
|||
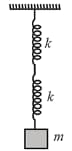 |
A trolley of mass , as shown in figure, is connected to two identical springs, each having spring constant equal to . If the trolley is displaced from its equilibrium position by and released, the maximum speed of the trolley is:
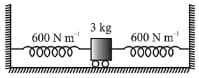
In the system shown in figure and pulley and threads are ideal. System is held at rest by thread Just after thread is burnt,
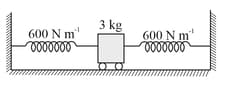
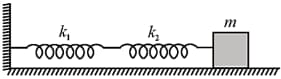
Two springs are connected to a block of mass placed on a frictionless surface as shown below. If both the springs have a spring constant then the frequency of oscillation of the block is